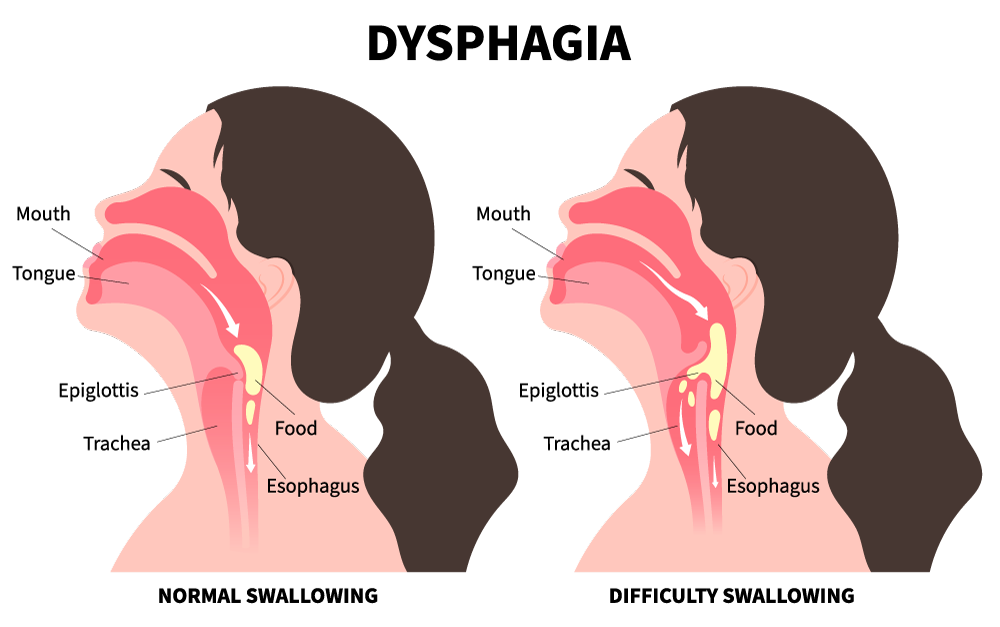
Have you ever experienced the unsettling feeling of food “going down the wrong pipe,” a sudden cough while taking a sip of water, or a persistent worry about choking during meals? These experiences, while sometimes dismissed as minor inconveniences, can be telltale signs of dysphagia, a medical term for difficulty swallowing.
Nearly 15 million individuals in the United States experience this challenge, a number that has grown dramatically in just the past decade. It is impacting people of all ages and backgrounds, highlighting the need for greater awareness and understanding.
What does dysphagia feel like?
The experience of dysphagia can vary greatly from person to person. Some common signs and symptoms include:
- Struggling to swallow solid foods, liquids, or both.
- Frequent choking or coughing while eating or drinking.
- The sensation of food or liquid getting stuck in the throat or chest.
- Pain or discomfort during swallowing (odynophagia).
- Unexplained weight loss or signs of malnutrition, which can occur due to reduced food intake from swallowing difficulties.
- Experiencing aspiration, where food or liquid enters the airways, potentially leading to pneumonia or other respiratory issues.
Causes of swallowing difficulties
Dysphagia isn’t a disease itself, but rather a symptom that can arise from various underlying conditions. Some of the common causes include:
- Neurological conditions: Disorders like stroke, Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and multiple sclerosis can disrupt the coordination required for swallowing.
- Head and neck issues: Tumors (both benign and malignant) or the effects of cancer treatment, such as radiation and surgery in the head and neck area, can damage the nerves and muscles crucial for swallowing.
- Acid reflux (GERD): Chronic backflow of stomach acid can irritate and scar the esophagus, potentially leading to swallowing difficulties.
- The aging process: Natural weakening of the swallowing muscles can occur as we age, sometimes making swallowing more challenging.
- Injury and trauma: Accidents or surgeries involving the head, neck, or throat can sometimes result in dysphagia.
Diagnosis dysphagia
If you or someone you know is experiencing swallowing difficulties, seeking professional medical advice is the first crucial step. Minnesota ENT physicians are experts in managing this process.
- Medical history review: First, we’ll ask questions about your symptoms, medical background, and any existing health conditions.
- Physical examination: Next, a careful examination of your mouth, throat, and neck will be conducted to look for any physical abnormalities.
- Imaging studies: In some cases, imaging tests like X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans might be ordered to visualize the structures involved in swallowing.
- Swallowing assessments: Specialized tests may be performed to assess your swallowing function directly. These may include:
- Videofluoroscopic Swallow Study (VFSS): A moving X-ray that shows how you swallow different foods and liquids. Helps spot problems like food going into the airway (aspiration).
- Fiberoptic Endoscopic Evaluation of Swallowing (FEES): A small camera views your throat as you swallow. Useful for seeing residue and how well you protect your airway.
Treatment and management strategies
Managing dysphagia often requires a team approach tailored to the individual’s specific needs. Common treatment and management strategies include:
- Speech therapy: A speech-language pathologist (SLP) plays a vital role in helping individuals improve their swallowing skills through specific exercises and techniques.
- Dietary modifications: Changing the texture and consistency of food and liquids can make swallowing easier and safer. This might involve pureed foods, thickened liquids, or other specialized diets.
- Swallowing exercises: Targeted exercises can help strengthen the muscles involved in swallowing and improve coordination.
- Medications: If an underlying condition like GERD is contributing to dysphagia, medications may be prescribed to manage it.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be recommended to improve swallowing problems. These typically aim to correct the physical issues that make it hard to swallow or find a different way for food to get to your stomach safely. This could mean opening up tight spots in your throat or food pipe, helping the muscles you use for swallowing work correctly, or making sure food and air go down the right pathways.
“The fear of choking or discomfort while eating is a significant concern for those with swallowing difficulties. As ENT specialists, we approach your situation with empathy and offer comprehensive evaluations and treatments to help alleviate these anxieties and improve your safety.”
Living with dysphagia
While living with dysphagia can present daily challenges, there are many ways to adapt and maintain a good quality of life:
- Practice mindful eating: Eating slowly, taking smaller bites, chewing thoroughly, and minimizing distractions can significantly aid the swallowing process.
- Choose wisely: Opting for softer, easier-to-swallow foods like yogurt, mashed fruits and vegetables, and well-cooked, tender meats can make mealtimes more manageable.
- Stay hydrated safely: Drinking adequate fluids is important, but your healthcare team can advise on the safest consistencies and techniques for fluid intake.
- Seek support and connection: Connecting with support groups or talking to healthcare professionals can provide valuable emotional and practical support.
Taking the next step
Concerned about swallowing issues for yourself or a loved one? Early diagnosis and appropriate management are key to improving both swallowing function and quality of life. The experts at Minnesota ENT are here to help.
Call us at 763-233-5755, text us at 763-265-6087, or visit MinnesotaENT.com to schedule an appointment and take the first step towards a clearer path forward.

